What is GPT‑5.2‑Codex? How Does It Differ from Standard GPT?
If GPT-5.2 is a Generalist, then GPT-5.2-Codex is a Specialist purpose-built for resolving complex programming challenges.
According to OpenAI’s latest blog post, GPT-5.2-Codex is not merely a standard GPT model fine-tuned on code data; it is the first model architecturally optimized for End-to-End Engineering.
Core Differences from Standard GPT:
- Contextual Persistence: Standard GPT models tend to “forget” previous definitions during lengthy conversations. In contrast, Codex possesses an ultra-long Context Window optimized for codebases, enabling it to understand cross-file dependencies.
- Execution, Not Just Generation: Standard GPT excels at writing “code snippets,” whereas GPT-5.2-Codex is designed to comprehend an entire Repository. During the launch, Sam Altman emphasized that GPT-5.2-Codex is not a simple autocomplete tool; it functions like a human engineer—reading documentation, locating error files, writing patches, and passing tests—allowing developers to execute tasks within real development environments.
Key Highlights: A Dual Leap in Data and Capability
The release of GPT-5.2-Codex has generated significant discussion within the technical community, primarily focused on three areas:
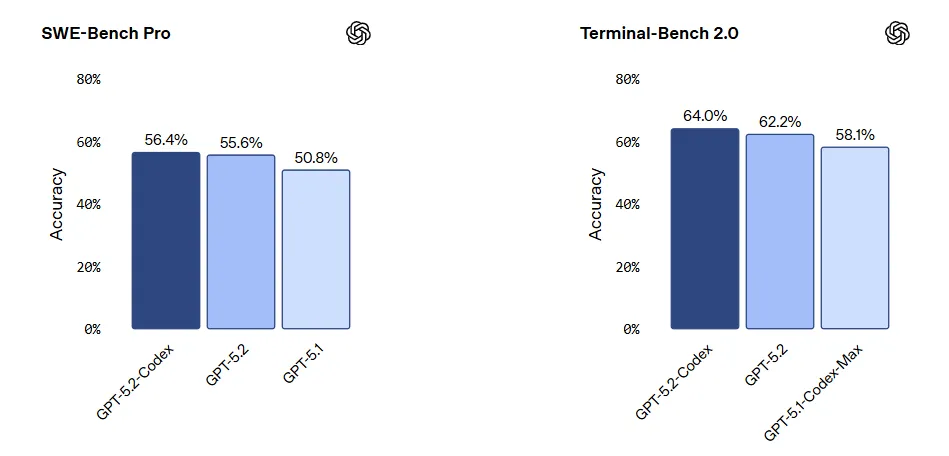
- Dominant Performance on SWE-bench Pro: SWE-bench Pro is currently the gold standard for measuring AI performance in resolving real-world GitHub issues. GPT-5.2-Codex achieved a historic score (resolving over 60% of issues), indicating it has moved beyond “Hello World” to fixing complex production-environment bugs.
- Self-Improving Loop: According to Ars Technica, OpenAI is internally using GPT-5.2-Codex to generate training data and optimize its own toolchain. This “AI training AI” recursive improvement model is accelerating iteration speeds beyond previous human expectations.
- Robustness per System Card: OpenAI’s System Card reveals significant improvements in handling “ambiguous instructions.” When requirements are unclear, the model is less prone to hallucination and more inclined to ask clarifying questions or use logical deduction to complete the context.
Deep Comparison: GPT-5.2-Codex vs. Claude Code
A frequently debated topic on social media is: “Which is better: GPT-5.2-Codex or Claude Code?”
We compare them across three dimensions: benchmark data, user experience, and use cases.
| Dimension | GPT-5.2-Codex | Claude Code (3.5 Sonnet / Opus) |
| SWE-bench Performance | S-Tier Demonstrates overwhelming dominance in resolving complex bugs involving multi-file dependencies. | A-Tier Performance remains strong, though it struggles slightly with ultra-long logical chains. |
| User Experience | “The Logic Beast” Users report impeccable performance in backend architecture, algorithm optimization, and mathematical logic, with minimal hallucination. | “More ‘Human'” Developers generally find Claude exhibits better “intuition” for Frontend UI, natural language interaction, and one-shot code generation. |
| Code Style | Rigorous & Engineered Tends to generate “Enterprise-grade” code featuring detailed comments and strict adherence to design patterns. | Concise & Intuitive Generates highly readable code that is better suited for rapid prototyping. |
| Ecosystem Integration | Strong Ecosystem Deeply integrated with GitHub Copilot and VS Code. | High Flexibility Performs exceptionally well in third-party editors like Cursor and Windsurf. |
Verdict: If your focus is backend refactoring, algorithm implementation, or large-scale system design, GPT-5.2-Codex is the clear choice. If you focus on frontend interaction or rapid prototyping, Claude Code may offer a superior experience.
Practical Application: A Guide to Boosting R&D Efficiency with GPT-5.2-Codex
Based on the engineering capabilities of GPT-5.2-Codex, we have outlined three core application scenarios and standard workflows within the modern Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
Scenario 1: System-Level Refactoring and Tech Stack Migration
Application Context: Managing technical debt involving massive file changes, such as major framework upgrades (e.g., migrating React Class Components to Hooks), infrastructure standardization (logging specs, security middleware integration), and dead code cleanup.
Standard Workflow:
- Step 1: Context Contextualization. Grant GPT-5.2-Codex read access to the entire Git repository via IDE plugins or CI/CD integration tools to establish a complete dependency index.
- Step 2: Constraint Definition. Input technical proposal documents to define refactoring boundaries.
- Command Example: “Maintain backward compatibility for V1 APIs. All database operations must go through the ORM layer; direct SQL concatenation is prohibited.”
- Pre-processing: Request the model to output a Refactoring Plan, listing affected modules, potential risks, and rollback strategies.
- Step 3: Iterative Execution & Review.
- Execution: The model submits Pull Requests by module.
- Verification: Trigger the automated testing pipeline (CI Pipeline) and feed failure logs back to the model for automatic correction.
- Acceptance: Human engineers perform the final Code Review, focusing on architectural soundness rather than syntax details.
Scenario 2: Full-Cycle Development and Automated Debugging
Application Context: Covers Feature Development and Bug Fixing, aiming to let AI handle implementation details while developers focus on logic orchestration.
Actual Workflow:
- New Feature Development (Enhanced TDD):
- Decomposition: Input the Product Requirement Document (PRD) and have the model convert it into a technical Task List.
- Code Generation: For each task, request the model to synchronously generate business implementation code and high-coverage unit tests.
- Bug Fixing (Root Cause Analysis):
- Input: Provide full Stack Traces, relevant log fragments, and involved source files.
- Analysis & Fix: The model performs cross-file attribution analysis to locate the Root Cause and generates a Patch.
- Regression Prevention: Mandate the model to write regression test cases to ensure the same logical error does not recur.
Efficiency Gain: Developers shift from spending 80% of their effort on code implementation to focusing on Requirement Clarification, Architectural Decisions, Edge Case Review, and Code Review.
Scenario 3: Frontend Engineering and UI Code Generation
Application Context: Suitable for rapid MVP (Minimum Viable Product) construction, internal tool development, and high-fidelity rendering of marketing pages.
Standard Workflow:
Step1: Visual Parsing: Input Figma design screenshots or preview links. GPT-5.2-Codex parses the DOM structure, component hierarchy, and layout parameters.
Step2: Code Generation:
- Structure Layer: Generates component skeletons compliant with project standards (e.g., React/Vue/Next.js).
- Presentation Layer: Generates atomic CSS (e.g., Tailwind CSS) or corresponding UI library code (e.g., Chakra UI/Ant Design).
Step3: Logic Completion: Developers connect backend API data and bind interaction events to the generated code.
Efficiency Gain: Significantly reduces time spent on Boilerplate Code, achieving a semi-automated flow from design to frontend implementation.
Safety and Practical Considerations
Despite its powerful capabilities, OpenAI’s System Card issues warnings that enterprises must heed during implementation:
- Overconfidence: When facing private frameworks it is unfamiliar with, the model may confidently provide incorrect code.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Although it has undergone red-teaming, there is still a risk of injection vulnerabilities in complex SQL queries or system calls.
- Best Practice: Always maintain a “Human-in-the-loop” approach. Do not allow AI to push code directly to production; manual Code Review remains the final line of defense.
The deployment of GPT-5.2-Codex marks a structural shift in Software Engineering. As traditional code implementation becomes highly automated, a developer’s core competency will be redefined as System Architecture Design and Technical Productization. This means developers must transition from “Code Executors” to “Technical Decision Makers,” orchestrating AI Agents to deliver complex engineering goals.
In the new normal of AI-Assisted Development, building a comprehensive intelligent tool ecosystem is key to improving organizational efficiency:
- Engineering Delivery Side: Rely on GPT-5.2-Codex to resolve hardcore technical issues such as underlying logic construction, algorithm implementation, and legacy system refactoring, ensuring the robustness of the technical foundation.
- Collaboration Management Side: Introduce iWeaver as the hub for unstructured data and workflows. It not only manages and converts information but also bridges departmental silos. iWeaver assists technical staff—as well as non-technical roles like Operations, Marketing, Sales, and Product Managers—in completing closed-loop management, from intent recognition and task breakdown to intelligent allocation and execution tracking, realizing seamless collaboration for Cross-functional Teams.